› MySQL 5.5 Community Server
› MySQL 5.6 Community Server
› Percona Configuration Wizard
› XtraBackup 搭建主从复制
Great Sites on MySQL
› Percona
› MySQL Performance Blog
› Severalnines
推荐管理工具
› Sequel Pro
› phpMyAdmin
推荐书目
› MySQL Cookbook MySQL 相关项目
› MariaDB
› Drizzle
参考文档
› http://mysql-python.sourceforge.net/MySQLdb.html
MySQL 相关项目
› MariaDB
› Drizzle
参考文档
› http://mysql-python.sourceforge.net/MySQLdb.html
这是一个创建于 2186 天前的主题,其中的信息可能已经有所发展或是发生改变。
mysql Ver 14.14 Distrib 5.7.25, for Linux (x86_64) using EditLine wrapper
CREATE TABLE `ttt` (
`uid` varchar(18) NOT NULL DEFAULT '',
`gap` int NOT NULL ,
PRIMARY KEY (`uid`),
KEY `gap` (`gap`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4 COMMENT='ccc_11332234';
insert into `ttt` values ('11111',1);
insert into `ttt` values ('11113',3);
insert into `ttt` values ('11115',5);
insert into `ttt` values ('11117',7);
insert into `ttt` values ('11119',9);
start transaction;
select * from `ttt` where `gap`=3 for update;
===============
另外一个客户端执行:
sql1: insert into ttt values ('22222',5);
sql2: insert into ttt values ('22233322',1);
阅读 mysql 技术内幕,其中对于 innodb 锁算法的时候看到,对于 1,3,5,7,9 数据存在的辅助索引,next-key locking 应该(-无穷,1] (1,3] (3,5] (5,7]... 在执行上述 for update 时候,查询的时候辅助索引所以会加上 (1,3]的锁,而且会在下一个索引值加上 gap lock(3,5), 同时主键 11113 会加上 record lock.
但是上述实际执行时 sql 2 会被阻塞.就是说(1,3]左边也是闭区间,为什么?
同时想问为什么这种 next-key locking 能解决幻读问题.?
(提前感谢大家的回答)
第 1 条附言 · 2019-09-20 15:11:20 +08:00
实际上对(1,3] (3,5) 加锁,同时,当 gap=1 时,同时对 uid>1111 加锁; 当 gap=5 时,对 uid<1111 加锁
1
cs8814336 OP mysql 技术内幕 innodb 存储引擎是在微信读书看的
|
2
cs8814336 OP 为什么这种 next-key locking 能解决幻读问题: 就是说 select * from `ttt` where `gap`=3 for update; 锁定了[1,5] 范围,假如他降级为行锁(就是辅助索引只锁 3,聚集索引还是会锁 11113 )会出现什么幻读问题?
|
3
wps353 2019-02-26 17:16:27 +08:00
首先:Next-key locking 是 gap lock 和 record lock 的统称,解决幻读问题是用 gap lock 来解决的。
Q:“为什么这种 next-key locking 能解决幻读问题: 就是说 select * from `ttt` where `gap`=3 for update; 锁定了[1,5] 范围,假如他降级为行锁(就是辅助索引只锁 3,聚集索引还是会锁 11113 )会出现什么幻读问题?” A:那如果此时再插入一条 gap=3 的记录,那就出现幻读了。 |
4
wps353 2019-02-26 17:18:46 +08:00
补充一下:Next-key lock 是前开后闭区间。
|
5
Wisho 2019-02-26 17:21:00 +08:00
@cs8814336
其实我也有点疑惑,如果根本不存在 next-key locking,全部都是 record lock 的话。辅助索引只锁 3,那么别的事务想插 3 也插不进来啊。那既然插不进来 3,怎么出现 phantom read 呢? |
6
kaid97 2019-02-26 17:22:04 +08:00
幻读是指比如我原先 GAP=‘ 5 ’的条数搜索出来有 2 条,现在因为别人插入,变成三条。所以间隙锁能解决幻读的原因就是要锁住 GAP 这个索引 B+树最下面叶子节点从第一条 GAP='5'出现到最后一条 GAP='5'出现那段。
总而言之就是要针对结果可能存在不唯一的时候采用间隙锁,锁住整段满足条件的。 Gap locking is not needed for statements that lock rows using a unique index to search for a unique row. (This does not include the case that the search condition includes only some columns of a multiple-column unique index; in that case, gap locking does occur.) For example, if the id column has a unique index, the following statement uses only an index-record lock for the row having id value 100 and it does not matter whether other sessions insert rows in the preceding gap: |
7
Wisho 2019-02-26 17:23:47 +08:00
@wps353
所以根源就在于“ Next-key locking 是 gap lock 和 record lock 的统称”吗? 感觉实际上真正生效的是一把 record lock。给 gap=3 上一把 record lock,不让别人插 3,就可以避免 phantom read 了,并没有下一段(3, 5]的 gap lock 什么事。 |
8
Wisho 2019-02-26 17:26:20 +08:00
@kaid97
感觉很多时候,关于“ repeatable read ”和“ phantom read ”的东西,大家讨论来讨论去,最后发现自己的理解是正确的,但是因为“名词”和“表述”上的不同,结果一堆人在那能吵一个下午= = |
9
Wisho 2019-02-26 17:31:26 +08:00
@cs8814336
只要锁住了 3,上了一把 record lock (当然对于底层来说,就是 B+树叶子节点里所有等于 3 的都给锁住了,可能是一条记录,也可能是一排记录),就不会有 phantom read 的问题了吧,毕竟在事务 1 里是用 FOR UPDATE 显式上了锁。 如果在事务 1 里没有显式上锁,且隔离级别还是默认的 RR,才有出现 phantom red 的可能性。 |
10
kaid97 2019-02-26 17:35:15 +08:00
我试了一下 0 是可以插的,因此锁的是(1,3]没错,后面插入的 1 是在原有的 1 之后的,所以就被锁了
[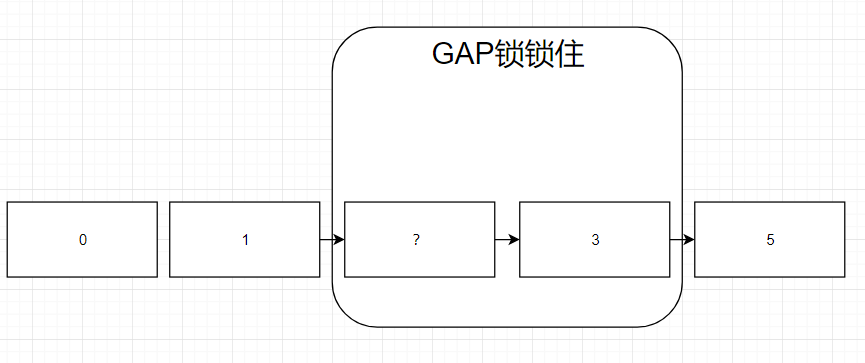]( https://i.loli.net/2019/02/26/5c75080e095ac.png) |
11
kaid97 2019-02-26 17:37:18 +08:00
@Wisho
Next-Key Locks A next-key lock is a combination of a record lock on the index record and a gap lock on the gap before the index record. https://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/8.0/en/innodb-locking.html#innodb-next-key-locks 官网文档有说 next-key-locks 是 record+gap |
12
wps353 2019-02-26 17:41:33 +08:00
@Wisho 你说的这种场景这么说是讲的通的。
比如这个场景: session 1:update ttt set gap=100 where gap<=3; (我觉得这点 MySQL 处理的有点粗暴,直接在底层 B+ 树上锁住区间) |
14
lxy42 2019-02-26 17:50:22 +08:00
[美团技术团队-Innodb 中的事务隔离级别和锁的关系]( https://tech.meituan.com/2014/08/20/innodb-lock.html)
|
15
lxy42 2019-02-26 18:13:35 +08:00
@Wisho #7
我的理解: 假如只对 gap=3 的记录加上行锁( record lock ),只能防止其它事务对这些记录的“写”操作,而不能防止 insert 操作。 考虑这样一种情景:事务 A 对 gap=3 的记录进行 update 操作,事务 B 此时 insert 了一条新的记录( gap=3 )。事务 A 接着 select 所有 gap=3 的记录,会发现多了一条记录而且这条记录“似乎”并没有被成功 update,这就是幻读。 |
16
Wisho 2019-02-27 05:08:39 +08:00
@lxy42
在默认的 RR 隔离级别下,事务 A 最后一次 select ... where gap = 3,是不会出现事务 B 刚刚插进去的那条的。 你想说的出现幻读应该是下面这样的吧?(默认 RR 隔离级别) t1. 事务 A select ... where gap = 3; 不显式加锁情况下,查出 N 条记录 t2. 事务 B insert 了一条 gap = 3 的新纪录,因为没有任何锁,所以成功插入了 t3. 事务 A 再次 select ... where gap = 3; 不显式加锁+RR 隔离级别,仍然查出 N 条记录( MVCC 提供的支持) t4. 最后事务 A update ... where gap = 3; 惊讶地发现 rows affected = N + 1,明明 update 前查出来的还是 N 行,为啥 update 的结果影响了 N + 1 行 这才是典型的幻读例子吧 |
17
cs8814336 OP @kaid97 的确从这个方向想是有一点道理. 那其实指的是锁住索引节点之间的空隙. 并不能单纯地想着锁住某个值. 但是假如这样想的话为什么会有 record lock 呢,既然有 record lock 的话他的确是能做到精确锁住某个值的,就是锁住了 b+树的非叶子节点的某个部分.(但是介绍说又说好像只能锁住 index record,除非 b+树的非叶子节点只有一种 value 的记录?)
官网文档有说 next-key-locks 是 record+gap: 的确是的. 但是官网也是说 next-key-locks 和 gap lock 是并列的 For locking reads (SELECT with FOR UPDATE or FOR SHARE), UPDATE, and DELETE statements, the locks that are taken depend on whether the statement uses a unique index with a unique search condition, or a range-type search condition. For a unique index with a unique search condition, InnoDB locks only the index record found, not the gap before it. For other search conditions, and for non-unique indexes, InnoDB locks the index range scanned, using gap locks or next-key locks to block insertions by other sessions into the gaps covered by the range. For information about gap locks and next-key locks, see Section 15.7.1, “ InnoDB Locking ”.[原文]( https://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/8.0/en/innodb-locks-set.html) |
18
cs8814336 OP @Wisho
@lxy42 innodb 的行锁都是在 index record 操作的,这个 index record 我可以理解为 b+树的非叶子节点吗? 假如是的话,gap=3 for update 理论上锁定的是整个 gap=3 的 index, 这样的话 gap=3 的新记录应该也是属于在 gap=3 的 index 下面的,假如只有 record lock 应该还是会锁住 gap=3 的 Record Locks A record lock is a lock on an index record. For example, SELECT c1 FROM t WHERE c1 = 10 FOR UPDATE; prevents any other transaction from inserting, updating, or deleting rows where the value of t.c1 is 10. Record locks always lock index records, even if a table is defined with no indexes. For such cases, InnoDB creates a hidden clustered index and uses this index for record locking. See Section 15.6.2.1, “ Clustered and Secondary Indexes ”. Transaction data for a record lock appears similar to the following in SHOW ENGINE INNODB STATUS and InnoDB monitor output: |
20
Wisho 2019-02-27 10:35:19 +08:00
@cs8814336 #17
感觉到了最后都会变成名词之争。要是面试的时候被问到了类似的问题,果断不能只说几个名词,感觉要滔滔不绝地把底层发生了啥都讲清楚= = |
22
mmdsun 2019-02-27 19:01:06 +08:00 via Android
https://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/5.7/en/innodb-locking.html
Record Locks:该锁是对索引记录进行加锁!锁是在加索引上而不是行上的。注意了,innodb 一定存在聚簇索引,因此行锁最终都会落到聚簇索引上。 Gap Locks:是对索引的间隙加锁,其目的只有一个,防止其他事物插入数据。在 Read Committed 隔离级别下,不会使用间隙锁,隔离级别比 Read Committed 低的情况下,也不会使用间隙锁,如隔离级别为 Read Uncommited 时,也不存在间隙锁。当隔离级别为 Repeatable Read 和 Serializable 时,就会存在间隙锁。 Next-Key Locks:这个理解为 Record Lock+索引前面的 Gap Lock。锁住的是索引前面的间隙!比如一个索引包含值,10,11,13 和 20。那么,间隙锁的范围如下 (negative infinity, 10] (10, 11] (11, 13] (13, 20] (20, positive infinity) 好早以前整理的笔记。忘记是从哪里摘的了。 |
24
junnplus 2019-06-02 20:50:42 +08:00
试了下,好像锁的不是 1,sql2: insert into ttt values ('1',1);这个就不阻塞
|
25
junnplus 2019-06-02 23:14:42 +08:00 锁了 ('11111',1)~('11113',3)这个区间的,所以 gap=1 的时候,uid 大于'11111'都会阻塞
|
27
phplin 2019-10-12 11:03:58 +08:00
我也遇到同样情况了,楼主找到原因了吗,为啥和 innodb 内幕书上说的不一样啊
|
28
cs8814336 OP @phplin 他这种应该是根据现有记录锁的.select * from `ttt` where `gap`=3 for update; 锁住的是
记录 insert into `ttt` values ('11111',1) 记为 A 记录 到 insert into `ttt` values ('11113',3) 为 B 记录 的区间 和 记录 insert into `ttt` values ('11113',3); 到 insert into `ttt` values ('11115',5) 记录为 C 区间 的区间. 只是粗略记作 (1,3] (3,5), 实际上是锁住比 A 记录大 到 B 记录的区间 和 比 C 记录小却比 B 记录大的区间。 比 A 记录 (11111,1 )大的记录,实际则是锁住 gap 非聚集索引 的 B+tree 在他右边的记录。 则实际上排序为 ('11111',1);('11113',3);('11115',5); 所以当 gap=1 时锁住了大于 11111 的区间,同理 gap=5 也被锁住小于 11115 的区间。 |